O Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) é uma tecnologia que permite ter diversas instâncias de Routing possibilitando ainda o overlap de endereçamento em simultâneo no mesmo router.
Este tipo de tecnologia é comum em MPLS nos Service Providers.
O VRF-Lite é uma versão mais básica do VRF, tendo por base o mesmo conceito. Para utilizar esta versão, não é necessário como pré-requisito a existência de uma rede MPLS.
Um dos exemplos comuns onde esta tecnologia é utilizada, é na segregação lógica de diversos clientes no mesmo equipamento.
O VRF funciona apenas em Layer 3, portanto deve ser configurado em interfaces físicas ou lógicas (SVI).
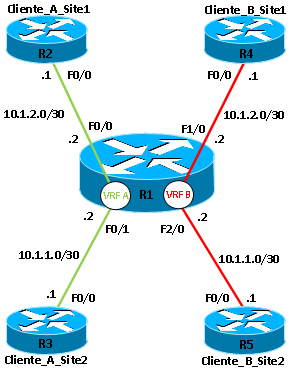 Com base na figura acima, toda a lógica da configuração foca-se no R1, nos restantes routers apenas será necessário configurar a respetiva interface e definir a default route.
Com base na figura acima, toda a lógica da configuração foca-se no R1, nos restantes routers apenas será necessário configurar a respetiva interface e definir a default route.
Configuração:
Configurar o VRF A no R1, a definição do RD é opcional
ip vrf A rd 100:100
Configurar o VRF B no R1, a definição do RD é opcional
ip vrf B rd 101:101
Configurar o endereçamento IP das interfaces e definir a VRF
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding A ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip vrf forwarding A ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip vrf forwarding B ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ip vrf forwarding B ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252
Verificar as diferentes VRFs e interfaces associadas
R1#sh ip vrf Name Default RD Interfaces A 100:100 Fa0/0 Fa0/1 B 101:101 Fa1/0 Fa2/0
Verificar a tabela de routing relativa a cada VRF
R1#sh ip route vrf * Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set Routing Table: B Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets C 10.1.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet1/0 C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet2/0 Routing Table: A Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2 i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets C 10.1.2.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 C 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
Testando a conetividade com o R3 apartir do R2
R2#ping 10.1.1.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/76/176 ms
Testando a conetividade com o R4 apartir do R5
R5#ping 10.1.2.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/49/72 ms
!Testando a conetividade com origem no VRF
R1#ping vrf ? WORD VPN Routing/Forwarding instance name R1#ping vrf A 10.1.1.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/39/96 ms R1#ping vrf B 10.1.1.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 4/33/64 ms R1#ping vrf B 10.1.2.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 24/36/60 ms R1#ping vrf A 10.1.2.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.2.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 8/33/80 ms R1#
LAB GNS3:
Encontra-se disponível para download o LAB sobre VRF-Lite.
Referências:
Cisco – Configuring VRF-lite
MPLS Multi-VRF (VRF-lite) – Multiprotocol Label Switching for VPNs (MPLS for VPNs)
Finalmente alguma coisa interessante por terras Lusas!